With the maturity of new energy vehicle technology and national policy subsidies, new energy vehicles will usher in explosive growth.
But when many friends buy new energy vehicles, their biggest concern is the inconvenience of charging. Charging piles are not popular in many cities. Today we will introduce the difference between our common AC charging pile and DC charging pile.
Principle of AC charging pile
The AC charging pile is essentially a socket with control, and its output is AC, which requires the on-board charger to transform and rectify itself. Limited by the power of the car charger, the power is generally small, mostly 3.3 and 7kw.
Functional characteristics of AC charging piles
(1) The human-computer interaction interface adopts a large-screen LCD color touch screen, which can choose fixed amount, fixed time, fixed amount, and automatic (until full) four charging modes; display the current charging mode, time (charging time, remaining charging time), Power (charge power, power to be charged) and current charging information.
(2) Support multiple payment methods such as credit card and scan code.
(3) Touch color screen display, friendly man-machine interface, convenient operation and maintenance.
(4) Rich communication interfaces, compatible with all vehicle BMS protocols and charging background protocols.
(5) Complete protection functions: overvoltage protection, undervoltage protection, overload protection, short circuit protection, leakage protection, etc.
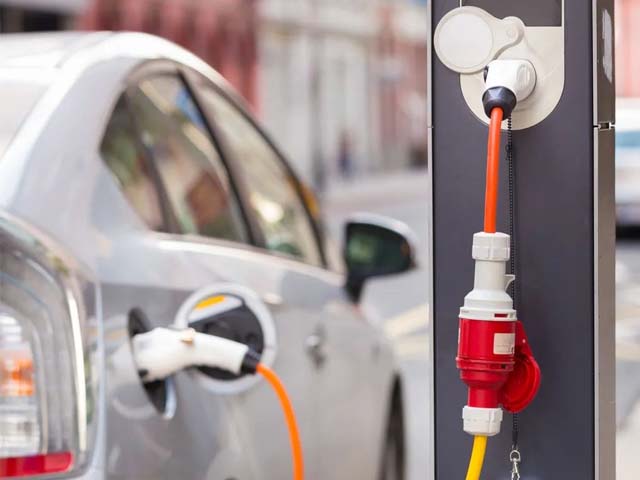

The difference between DC charging pile and AC charging pile
DC charging pile: DC electric vehicle charging station, commonly known as "fast charging", is a power supply device that is fixedly installed outside the electric vehicle and connected to the AC power grid to provide DC power for the non-vehicle electric vehicle power battery.
The input voltage of the DC charging pile is three-phase four-wire AC 380V±15%, the frequency is 50Hz, and the output is adjustable DC, directly charging the power battery of new energy vehicles.
Since the DC charging pile adopts a three-phase four-wire system for power supply, it can provide sufficient power, and the output voltage and current can be adjusted in a wide range, which can meet the requirements of fast charging.
AC charging pile: AC electric vehicle charging pile, commonly known as "slow charging", is fixedly installed outside the electric vehicle and connected to the AC grid to provide AC power for the electric vehicle on-board charger (that is, the charger that is fixedly installed on the electric vehicle) Power supply device.
The AC charging pile only provides power output and has no charging function. They need to be connected to the car charger to charge the electric car. It is equivalent to just playing the role of controlling the power supply.
The difference between the two: In simple terms, the AC charging pile requires an on-board charger to charge, while the DC fast charging pile does not require this device.
The charging speed differs greatly between the two. After a pure electric vehicle (normal battery capacity) is fully discharged, it takes 8 hours to fully charge through the AC charging pile, while it only takes 2-3 hours to fully charge through the DC fast charging pile.
The AC charging pile provides power input for the charger of the electric vehicle. Due to the low power of the car charger, fast charging cannot be achieved.